What is Technology Transfer?
To transfer federally-funded technologies to another organization for commercialization

What is a patent?
- A patent is a document granted by a governing body that confers an exclusionary right to an inventor to make, use, and sell the invention claimed in the patent for a set time period
- A person is an inventor on a patent if they contributed to conceiving at least one claim on the patent application
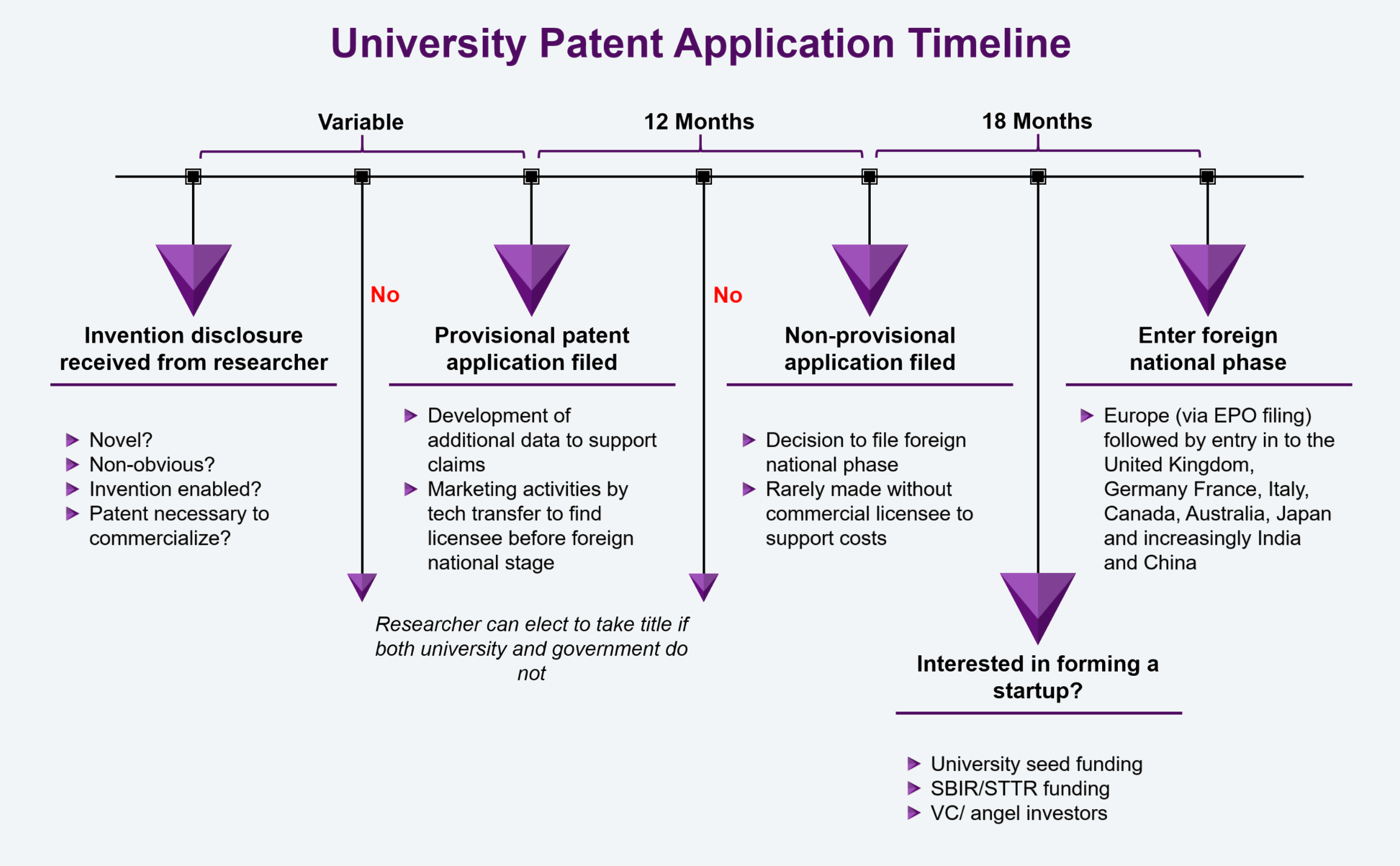
- Patent prosecution: Takes 3-4 years to 7-8 years from filing before patent issuance. Patent maintenance fees are paid at 3.5, 7.5, and 11.5 years.
Provisional vs non-provisional patent
- Provisional Patent Applications: The “first stop” in the patent prosecution process. Not a patent! Can be used to add data developed in the 12 months between filing and conversation
- Non-provisional Patent Applications: Patent life is 20 years from filing date of the earliest non-provisional U.S. patent application
- License agreement: An agreement that grants a third party (the licensee) a package of rights to allow them to use an intellectual property asset for specific purposes. Does not prevent licensed intellectual property from being used for non – commercial academic research, teaching, and patient care purposes.
- License revenue/ royalty: ~ 40% of net license revenue will go to inventors (percent varies by institution)
Utility patent requirements
- Novel – must not be described in a prior art reference anywhere in the world
- Non-obvious – should demonstrate that the invention produced some “unexpected” result that would not have been anticipated by prior art
- Useful – patent claiming therapeutic use in humans can be rejected if there is insufficient data from relevant animal model systems. Generally, a licensing associate/manager assigned to handle specific subject matter will work with investigators to assess, market and license inventions/ intellectual property
Other Important Terminology
- Trade secrets are information, processes, techniques, designs, or other knowledge not generally understood or made public, which provide the holder with a competitive advantage in the marketplace. When it comes to protecting important manufacturing processes, trade secrets can be more important than patents since patents will disclose such processes on publication
- Freedom to Operate (FTO)–Receiving a patent does not guarantee that an inventor is free to make, sell or use it. A new technology only has freedom to operate if the features of the technology are free and clear of valid claims from patents that are still in force in the country in question. IP lawyers will conduct a thorough FTO analysis for a fee, but startup founders should conduct a preliminary prior art search
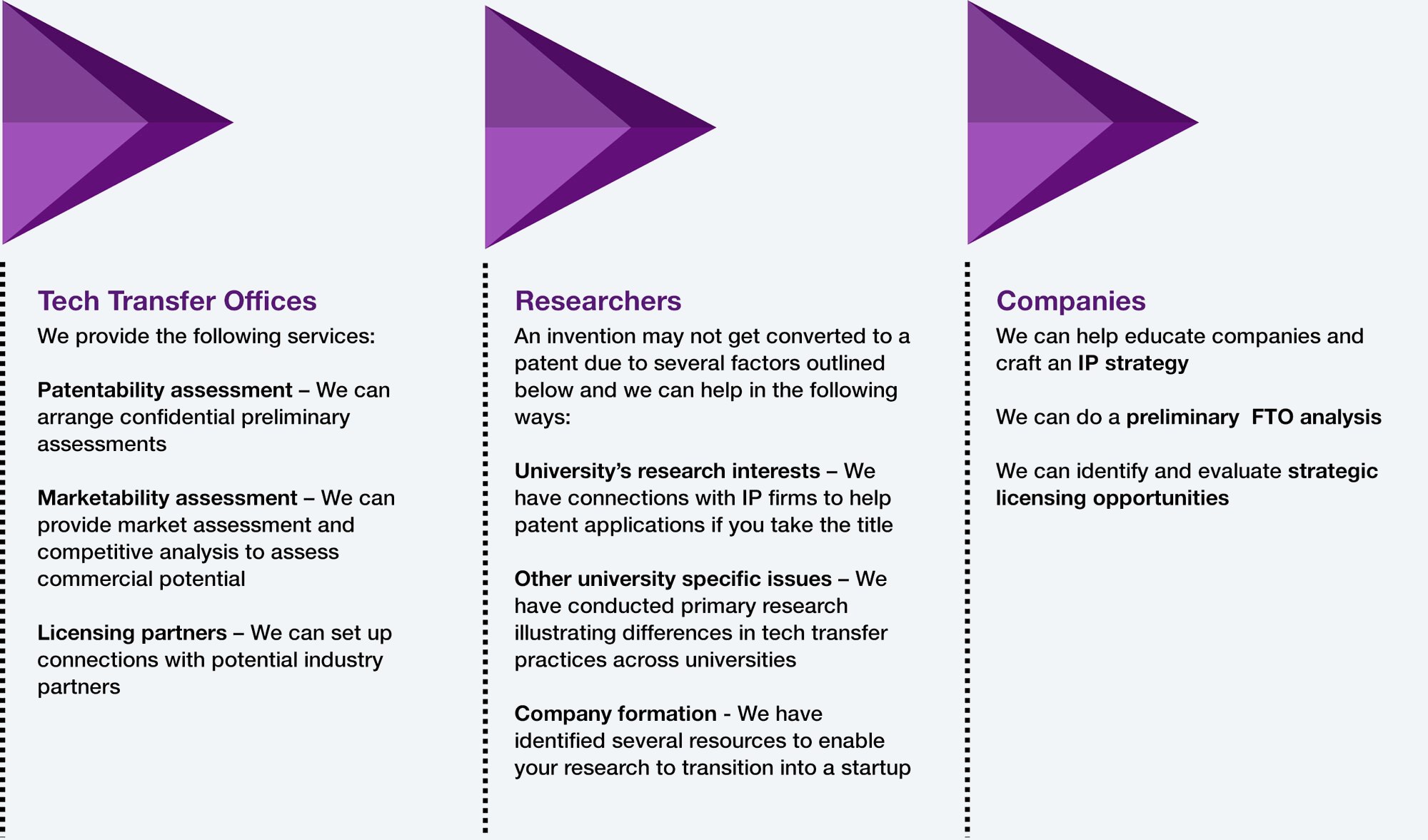
How we work with Tech Transfer Offices, Academic Researchers and Companies
We will act as a liaison to overcome bandwidth challenges on both ends and provide tailored recommendations